PROJECT: StardyTogether
StardyTogether is a desktop contacts and venues manager application specially for NUS students to help them find free time and rooms to study together with their friends.
Most of the user interactions are via CLI, while there exists a GUI created with JavaFX. It is written in Java and has about 6kLoC.
The source code is based on the AddressBook-Level4 project created by SE-EDU initiative.
Code contributed: [Functional code]
[Test code]
Feature Contributions
-
Major enhancement: Customized alias
-
What it does: Allows students to create their own aliases for all the commands and delete/unalias their created aliases if they do not want them anymore.
-
Justification: This feature makes the use of CLI much more convenient as students can now type faster and in their own style. It improves the overall user experience from using the application as it makes it more personalized and user-friendly.
-
-
Minor enhancement: Vacant Room Finder logic, parser and UI
-
What it does: Shows the vacant rooms in the building that the student is searching for for the day.
-
Justification: This allows students to easily find empty rooms for them to study in with their friends. Since students can have many pockets of free time in school, this feature displays the schedule of the rooms for the whole day so that students to plan their study venue.
-
-
Minor enhancement: Google Maps location and direction navigator
-
What it does: Finds the location of the specified address or the directions from place to place. This navigator recognises NUS building names and finds their respective locations, which makes it convenient for students to search for NUS venues.
-
Justification: This allows students to find their way in NUS easily by searching for the buildings' common names rather than their postal codes or addresses.
-
-
Other contributions:
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Adding a command alias: alias (since v1.1)
To create customized aliases for any valid command, you can enter the command alias followed by your desired command and your very own alias.
Format: alias [COMMAND] [ALIAS]
Examples:
-
alias find f -
alias alias al
Removing a currently existing alias: unalias (since v1.3)
To remove a previously created alias, you can enter the command unalias followed by the alias you wish to remove.
Format: unalias [CURRENT_ALIAS]
Examples:
-
unalias f
Vacant study rooms finder : vacant (since v1.3)
To get a list of study rooms in the specified building and their vacancy (in blocks of 1 hours), you can enter vacant follwed by the BUILDING code.
Format: vacant BUILDING
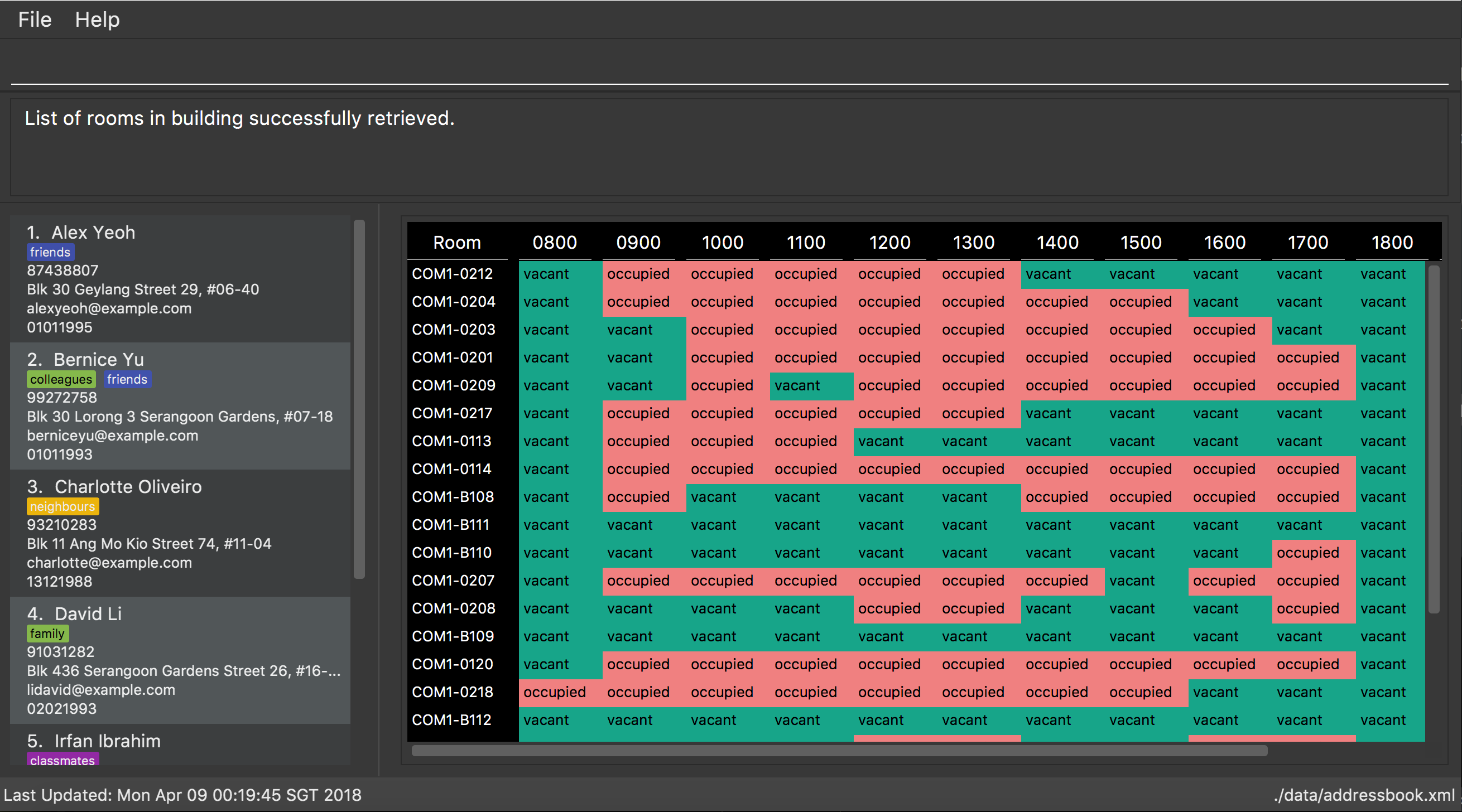
The building must be in NUS venue format, e.g. COM1, S17, E2
|
Examples:
-
vacant COM1
Finds the vacancy status of study rooms in COM1 building.
Google maps display : map (since v1.4)
To find locations or a path from one place to another, you can enter the command map along with the locations to launch Google Maps with the specified location(s).
Format: map LOCATION or map LOCATION/LOCATION… or map current location
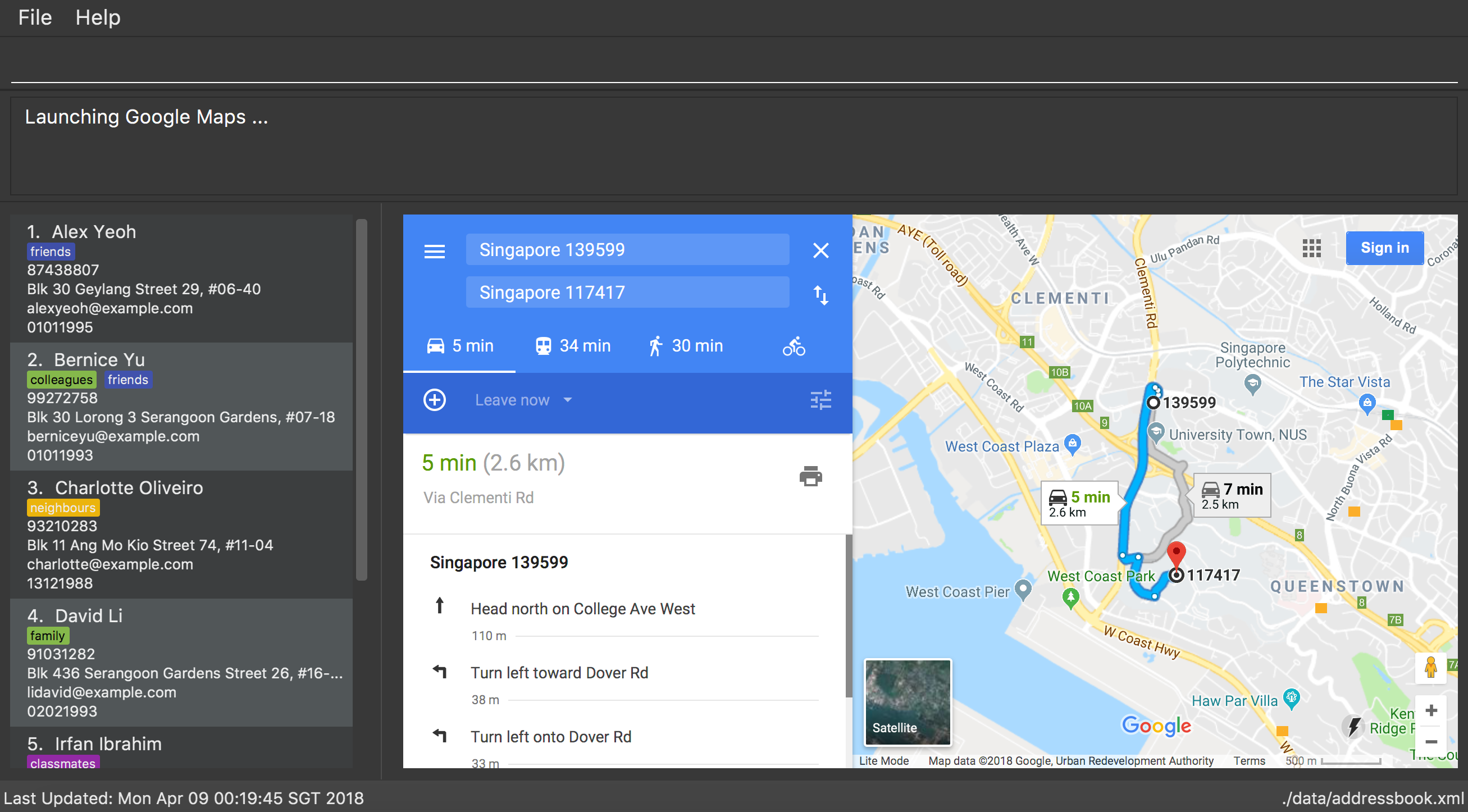
Examples:
-
map current location
Displays your current location on the map. -
map BIZ1
Displays the location of BIZ1 (which is an NUS building name). -
map Tampines Mall/COM1
Displays the directions fromTampines MalltoCOM1. -
map Tampines Mall/COM1/Airport Blvd
Displays the directions fromTampines MalltoCOM1toAirport Blvd.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
Customized Alias feature
Current Implementation
The alias mechanism is maintained in a HashMap which resides in UniqueAliasList in the Model component. It supports the undoable command.
The alias as specified by the user is used as the key in the HashMap, with its respective command as the value.
Whenever a user enters a command, the application will be able to check if the command is a previously-set alias efficiently by using the API provided by the UniqueAliasList.
If the input command word is an existing alias, it will be replaced with its respective command as shown below.
public String getCommandFromAlias(String aliasKey) {
if (aliases.contains(aliasKey)) {
return aliases.getCommandFromAlias(aliasKey);
}
return aliasKey;
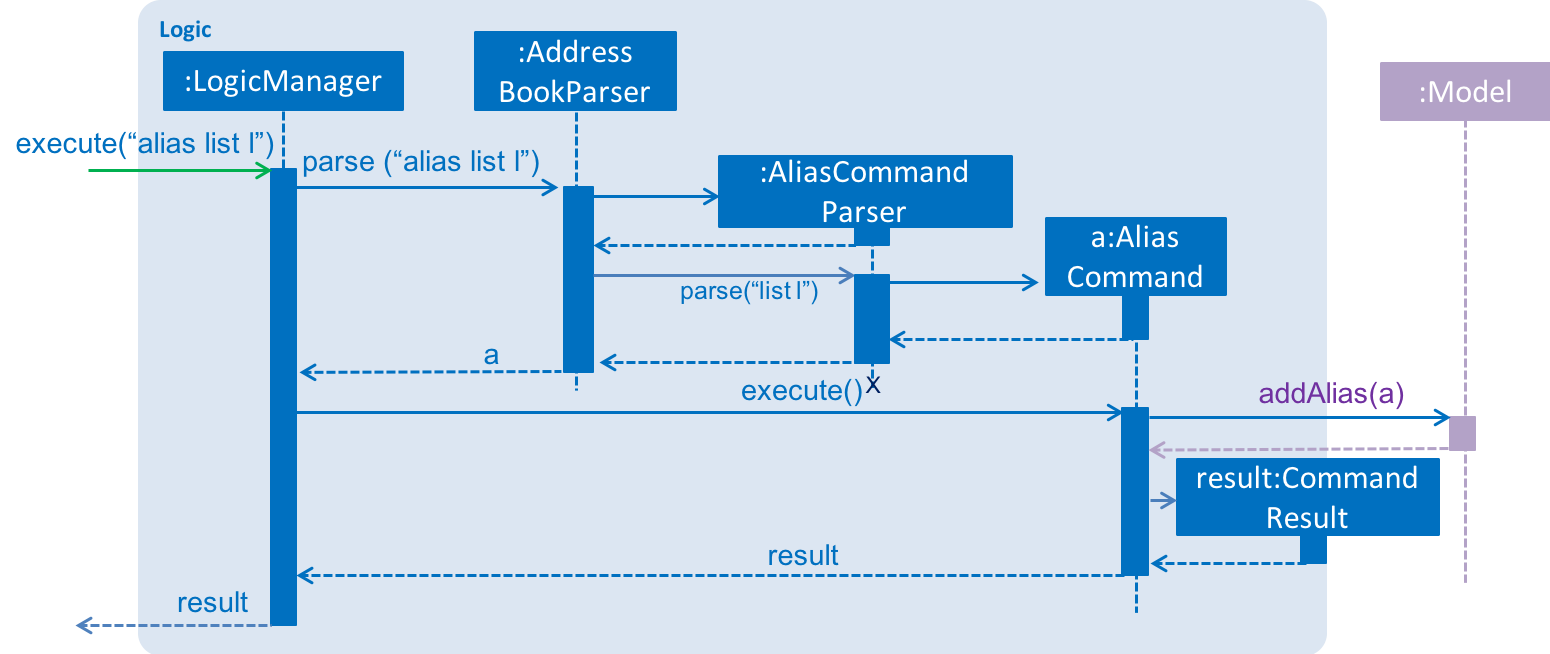
}When the user creates a new alias for a command, the AliasCommand checks that the command is a valid command, and the alias is not an existing application command word.
The following sequence diagram shows how the AliasCommand works:
Design Considerations
Aspect: How alias list is maintained
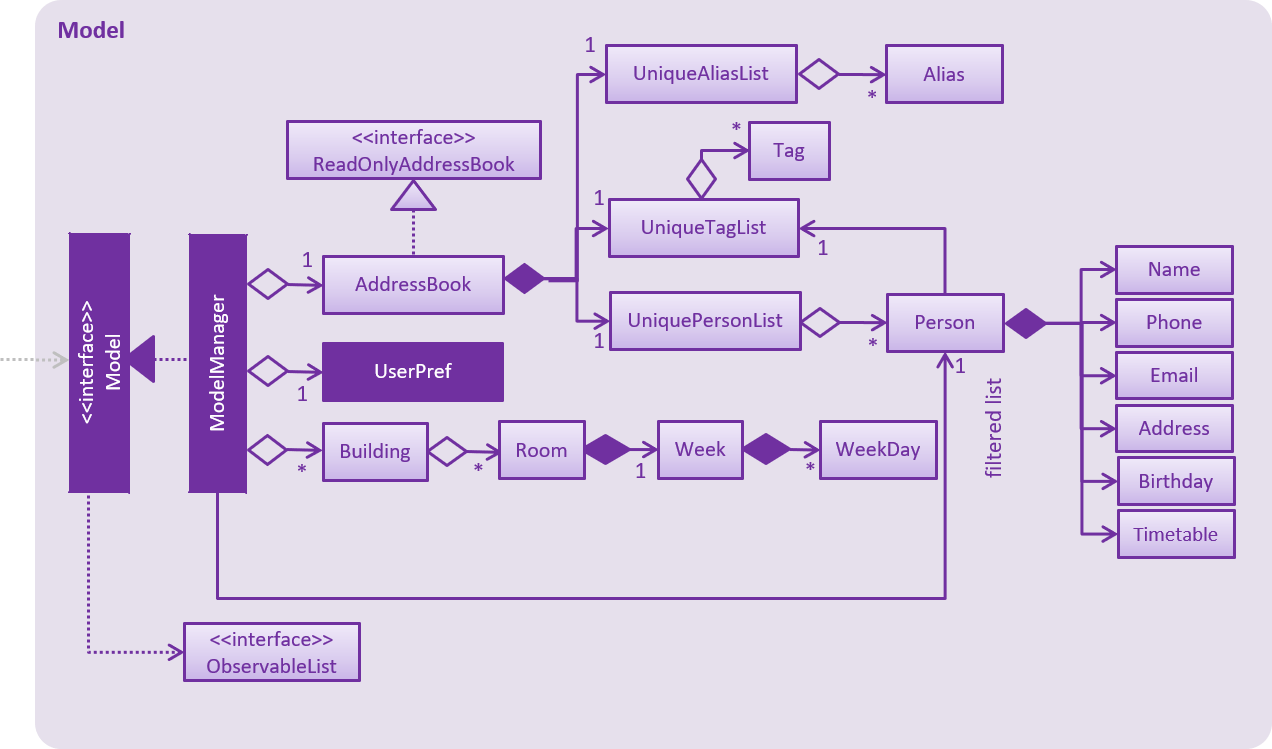
The alias list is maintained in a UniqueAliasList which is stored in the Model component.
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Create an
UniqueAliasListin thealiasmodel-
Pros: Reduce coupling between
Aliasand other commands. This design follows the Open Closed Principle where a command is open to extension and closed to modification. -
Cons: More difficult to implement as need to design an instance of a
UniqueAliasList.
-
-
Alternative 2: Create a HashMap of
Aliasin each command class-
Pros: Faster to implement as each command class only needs to include a HashMap that stores all the aliases tagged to the command.
-
Cons: High coupling between
Aliasand other commands and the HashMaps of every command needs to be iterated through to find to find the aliased command.
-
Aspect: How alias is stored
The following class diagram shows how the aliases are stored:
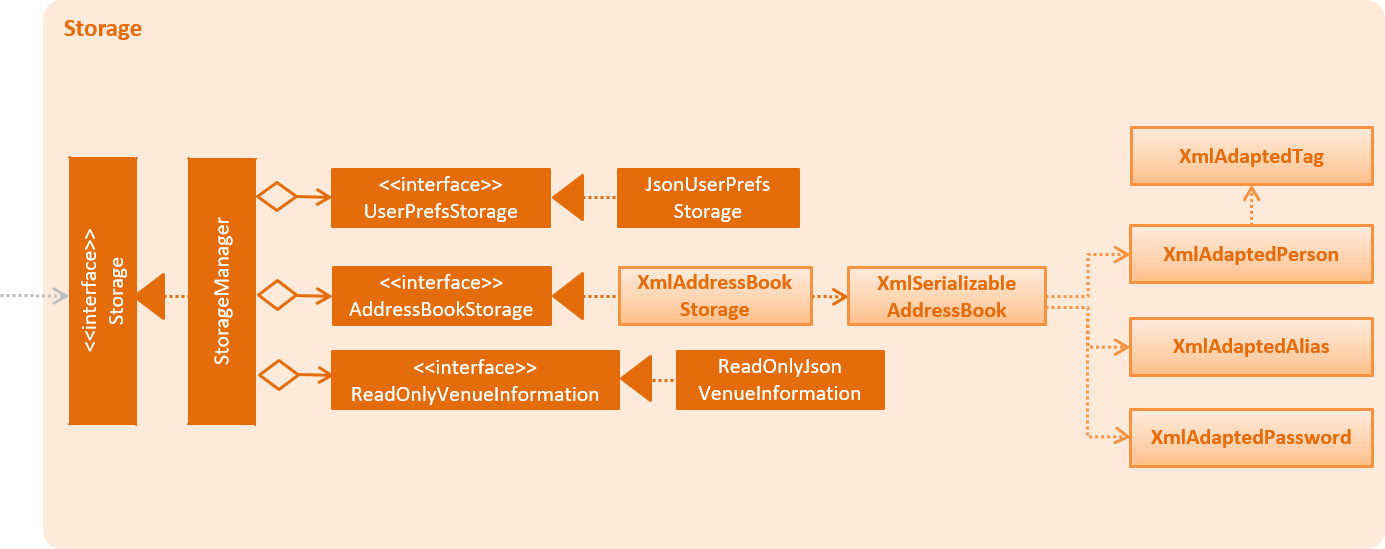
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Store as
XmlAdaptedAliasand save toaddressbook.xml-
Pros: Reduces files where data need to be stored, as all the user saved data is in one file.
-
Cons: Need to design a section in
addressbook.xmlfor saving alias data with the other data like person data.
-
-
Alternative 2: Store in
UserPrefsStorage-
Pros: Easier to implement.
-
Cons: Affects Import command, to import
UserPrefsStorageas well, than just importingaddressbook.xml
-
Aspect: Displaying stored aliases
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use the original
listcommand to display aliases-
Pros: Utilizes unused
infoPanelspace in the UI. -
Cons: Need to integrate with the
ListCommand.
-
-
Alternative 2: Modifying
AliasCommandto supportalias listcommand-
Pros: Easier to implement as only modification of the command is required.
-
Cons:
alias listshould not be an undoable command, and conflicts with theAliasCommand.
-
Vacant Room Finder feature
Current Implementation
We are using Venue Information JSON file from NUSMods to retrieve the weekly timetable of the venues. To increase the performance of retrieving the timetable of the venue, we decided to download Venue Information JSON file and have an offline copy stored in our StardyTogether application.
We have added the list of NUS buildings and the list of rooms in each building into the offline copy.
We use ReadOnlyJsonVenueInformation, which resides inside Storage to read and store the room timetable data inside nusVenues in Room class, and also store NUS Buildings and their respective rooms inside nusBuildingsAndRooms in Building class.
To avoid reading the data from Venue Information JSON file whenever the vacant command is executed, we only read the data once when the MainApp starts.
ModelManager will checks if the building is in the list of NUS Buildings, and will throw BuildingNotFoundException if the building is not in the list of NUS Buildings.
We have created Building, Room, Week, and WeekDay in Model to read and store all weekday schedule of all NUS Rooms.
The following architecture diagram shows the model component:

The following sequence diagram shows how the logic component of Vacant Room Finder works:
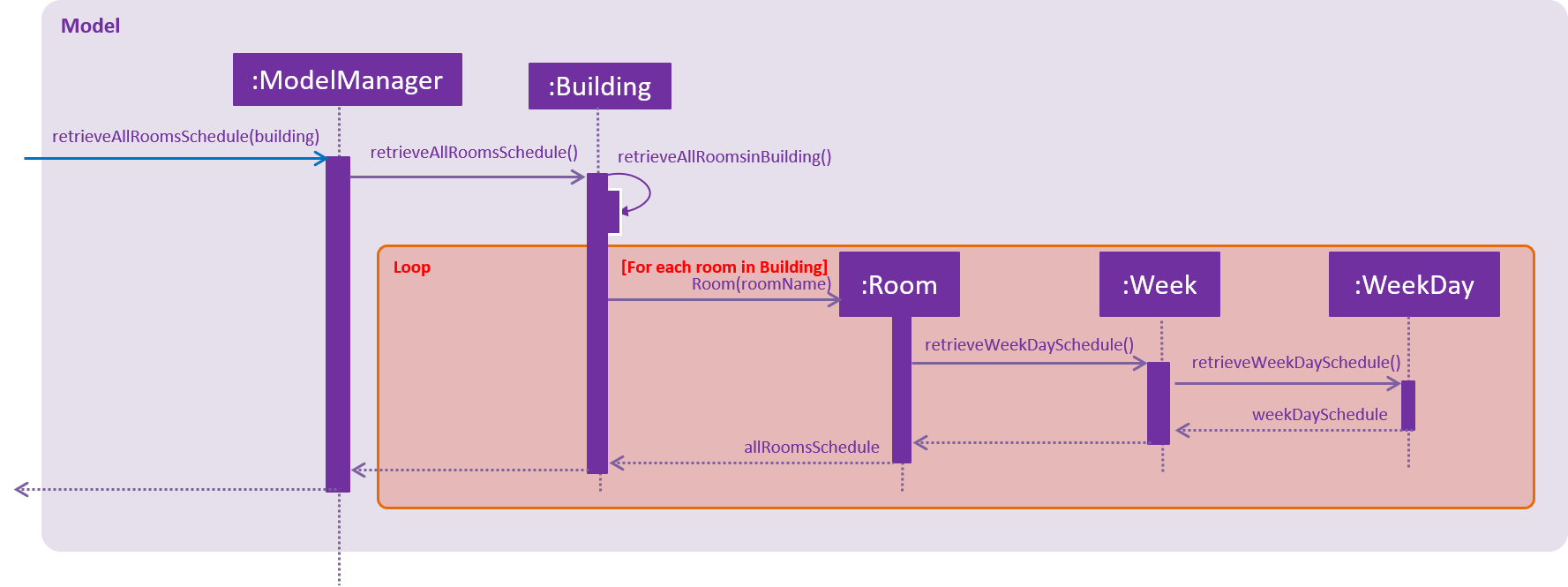
As shown in diagram above, all Rooms weekday schedule will be return in an ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> data structure. This result will be shown to the UI on the InfoPanel
Aspect: Shows list of vacant rooms
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Displays a list of rooms and the weekday schedule from 0800 to 2100
-
Pros: User is able to see which rooms are vacant throughout the day
-
Cons: User has to manually find which rooms are vacant at the current time
-
-
Alternative 2: Displays a list of vacant rooms at the current time
-
Pros: User is able to see which rooms are vacant at current time immediately
-
Cons: User is not able to see the room schedule for the whole day
-
Aspect: Design of converting JSON to objects
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Create a Building, Room, Week and Weekday class
-
Pros: Follows the Single Responsibility Principle where each class should have responsibility over a single part of the functionality provided by the software
-
Cons: More difficult to implement as the design of the flow of work between classes has to be thought out
-
-
Alternative 2: Create a static list of rooms in the Building class which has a room schedule for the day
-
Pros: Code is shorter
-
Cons: The Room and Building class will have schedule-related code which makes the classes messy.
-
Google Maps feature
Current Implementation
We are using the Google Maps Browser and passing the location(s) specified by the user into the URL, and then connecting to the internet to retrieve the Google Maps with the respective location(s). We have implemented two functionalities for the Google Maps: Address locator and locations navigator.
-
For one location specified, the "https://www.google.com/maps/search/" URL prefix is used.
-
For more than one locations specified, the "https://www.google.com/maps/dir/" URL prefix is used.
When a location specified by the user is an NUS building e.g. S1, our application compares the input with the list of NUS buildings to check from, and recognizes it as an NUS building.
The location is replaced with its respective postal code and passed to form the Google Maps URL.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Google Maps implementation
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use Google Maps in browser
-
Pros: Does not require a re-setup of project to link with the Google API.
-
Cons: Browser mode (Google Lite Maps) does not support some advanced Google Maps features. (But these additional features are not used in this project and thus having the browser implementation fulfils the intended functionality)
-
-
Alternative 2: Use Google Maps API
-
Pros: Google Maps in the application will have the complete set of features.
-
Cons: May cause a longer loading time for the application and Google Maps browser.
-
Aspect: Saving NUS buildings' addresses
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saving the postal codes of NUS buildings in the Building class
-
Pros: Easy to implement. Since there is only one set of fixed NUS buildings and postal codes, both can be stored as lists in the same class.
-
Cons: Need to have a method that finds the correct postal code for a building from the lists.
-
-
Alternative 2: Creating a new class to store postal codes/addresses of NUS buildings
-
Pros: The code looks neater. Every building will have an
Addressclass to store their postal codes/addresses. -
Cons: Need to maintain a
Buildinglist, where eachBuildingcontains theAddressclass.
-